Introduction
Human Resources Management is a vital activity in any organization. People are the greatest assets to a company or organization. Human Resources Management is a strategic approach to effectively and efficiently managing the employees in an organization. Human Resource Management is the process of employing people, training them for specific roles, remunerating them for their performance, developing policies for their well being, and strategizing to retain them.
The HR department acts as a liaison between the employer and the employees. The HR team helps to maintain the organizational structure of the workplace and ensures safe and efficient performance of the jobs. HR management holds many responsibilities and in this article, we will briefly touch on the functions of the HR department and fully focus on laws and regulations that companies have to comply with to be fully compliant.
Functional areas of Human Resources Management
HRM activities involve Hiring and Recruitment, Training, and development, maintaining Employer-Employee relationships, instilling and maintaining the company culture, handling the benefits and compensations due to the employees, handling indiscipline, and managing compliance issues. The focus of a company is to generate revenue and this can be achieved by, utilizing the skills and abilities of people. HRM play a critical role in achieving this.
Hiring and Recruitment
Recruiting the best talent and retaining them is the top priority of many organizations. Similarly hiring to fill a role is a vital activity that is an ongoing process in any organization. The HR department plays a critical role in the hiring and recruitment process. The HR team works very closely with the other department heads or supervisors to identify the needs. The recruitment strategy is formulated and the HR team handles all activities like placing advertisements, screening applications, and interviewing the candidates.
Training and development
Retaining talent is a very critical task for all organizations, and the HR team performs this critical task. The HR department to help employees to prepare for career advancements within the organization initiates Training and Development programs. This will assist in retaining talent and will benefit both employers and employees. This would usher in higher productivity and lower turnover rates. This also encourages job satisfaction and boosts the employees’ confidence in the organization.
Employer-Employee relationship
Maintaining a healthy employer-employee relationship contributes not only to the growth of the company but also creates greater trust in the management. The HR department is the liaison between the employer and the employees and will help mitigate any disagreements.
Amicable settlement of all employee grievances whether regarding benefits, compensation, work hours, workload, etc are achieved through consultations, thus creating a positive work atmosphere. This is vital for the growth of the company.
Maintaining Company Culture
Company culture may vary from company to company. The HR department may share the company’s values, vision, and rules with the employees during the onboarding process. Maintaining company culture means being able to identify any shortcomings within the organization and being able to address them for better functioning of the company. The HR team addresses these shortcomings effectively.
Benefits and Compensation
Though it is an administrative task, the HR departments oversee both the mandated and voluntary company benefits. Employees contribute towards social security, unemployment, and workers’ compensation are mandated benefits, whereas other benefits like paid time off, disability income, etc are voluntary. They serve as additional incentives to the employees, both potential and current. HR managers are fully aware of the company benefits policy and are capable of clearly explaining this to the employees.
Handling indiscipline
The HR team is highly experienced and is, therefore, well equipped to handle indiscipline. Disciplinary action like issuing show cause notices, and termination are delicate issues and have to be handled fairly and consistently to prevent escalations. HR Managers must have a clear system in place to hold employees accountable. They should be able to consult with legal counsel to ensure they are well within the law in the handling of disciplinary issues.
Complying with Laws and Regulations
Statutory Compliance requirements have to be fully complied with by all companies that employ 10 or more employees. The Government enacts these rules and regulations to safeguard the interests of the employees by providing healthy working conditions and ensuring fair work practices.
The HR teams are entrusted with the task of seeing that the company is fully compliant with all the statutes, rules, and regulations. The government keeps tweaking these rules very often and the onus is on the HR team to update these changes.
These are some of the more important functions of Human Resource Management. We shall now proceed to the Labour Laws and Regulations that are to be managed by the Human Resource Management team.
Labour Laws and Rules
Labour Laws are a body of laws, administrative rulings, and precedents that address the legal rights of working people and the restrictions on their organizations. These laws define the rights and obligations of workers and employers in the workplace. Labour Laws arose due to the demand of employees for better working conditions, and their right to organize. From the employer side, the demand was to restrict the power of workers in many organizations and to keep labour costs down.
A wide number of Labour Laws were legislated and it was made mandatory for companies or organizations to strictly follow them. Companies, especially those employing a large number of employees look upon their Human Resources Management teams to handle these laws and keep the company compliant.
The role of the HR team becomes vital as these are subject to frequent changes, and therefore, there is a need for constant updation at the administrative level.
However, the Ministry of Labour and Employment, Government of India, introduced 4 Bills in 2019 to consolidate 29 of the existing labour laws into 4 Codes. These Codes or Reforms hope to empower the worker, both in the organized and unorganized sectors, and safeguard their interests.
These 4 Labour Codes are:
- The Code of Wages, 2019
- The Code of Social Security, 2020
- The Industrial Relations Code, 2020 and
- The Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020
1. The Code of Wages, 2019
The Code of Wages, 2019 subsumes the following 4 Acts.
1. The Payment of Wages Act, 1936
The objective of this Act is to regulate the payment of wages to employees in time without delay and deduct the mandated contribution from the employees, and the employers under the provisions of the Act.
2. The Minimum Wages Act, 1948
The objective of the Minimum Wages Act, 1948 is to secure minimum wages for all the workers whether skilled or unskilled in the scheduled employment. It hopes to safeguard employees and prevents exploitation by employers.
3. The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965 provides the payment of bonus to persons employed in certain organizations, employing 10 or more employees, based on profit or productivity. The objective is to impose a legal responsibility upon the employer who is covered by the Act, to pay Bonus to their employees as an incentive.
4. The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976
The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976 provides for the payment of equal remuneration to men and women employees without discrimination on grounds of gender.
2. The Social Security Code, 2020
The Social Security Code has subsumed the following 9 Acts:
1. The Workmen’s Compensation Act, 1923
The Workmen’s Compensation Act, 1923 provides workers employed in certain industries compensation for injuries suffered during employment and to make good the losses.
2. The Employees State Insurance Act, 1948
The Employees State Insurance Act, 1948 is an Act to provide certain benefits to employees in the event of some eventualities like sickness, maternity, and employment-related injury.
3. The Employees Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952
The Employees Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952 were enacted to provide social security to employees. Through this Act, the Employees Provident Fund was set up to provide a post-retirement benefit for the employees or their legal heirs in case of the death of the employee. The Act provides for the institution of provident fund, pension fund, and deposit-linked insurance fund for employees employed in establishments that come under the purview of the Act.
4. The Employees’ Exchanges (Compulsory Notification of Vacancies) Act, 1959
The Employees’ Exchanges (Compulsory Notification of Vacancies) Act, 1959 provides for compulsory notification of vacancies to the Employment Exchange and the submission of returns relating to employment by the employer.
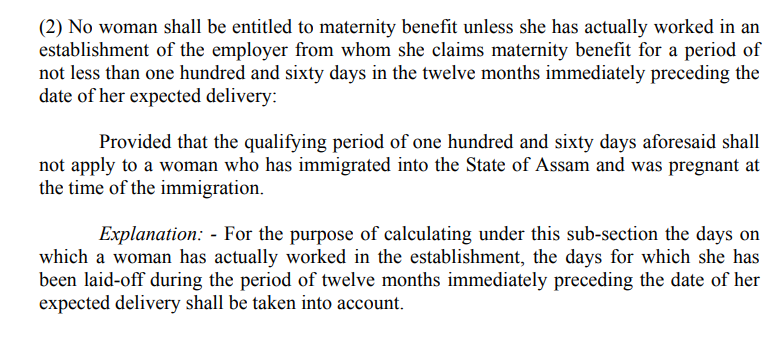
5. The Maternity Benefit Act
The Maternity Benefit Act was enacted to regulate the employment of women at the time of their maternity. The Act entitles women employees to’ maternity benefit’ which is fully paid wages during the pre-maternity and post-maternity period. Women employees are eligible for maternity leave for 26 weeks.
6. The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
The Payment of Gratuity Act provides for the payment of gratuity to employees as a token of appreciation for their contribution to the company. It is a monetary benefit provided to employees employed in mines, factories, plantations, oil fields, ports, and other establishments after their retirement.
The gratuity is 15 days’ salary for every year of employee service subject to a maximum of rupees ten lakhs.
7. The Cine-workers Welfare Fund Act, 1981
The Cine-workers Welfare Fund Act, 1981 was enacted to provide for the levy and collection of a cess on feature films to finance the activities to promote the welfare of certain cine-workers. Workers covered under the Act received monthly remuneration of not less than Rs:8000/-.
8. The Building and other Construction Workers Welfare Cess, 1996
This Act was enacted to regulate the employment and condition of service of building and other construction workers and to provide for their safety, health, and welfare measures and other matters connected therewith.
9. The Unorganized Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008
The Unorganized Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008 enables the formulation of Welfare Schemes for the workers of the unorganized sector. This welfare scheme covers health and maternity benefits, life and disability cover, old age protection, etc.
3. The Industrial Relations Code, 2020
The Industrial Relations Code, 2020 subsumes the following 3 Acts:
1. The Industrial Disputes Act, 1942
The Industrial Disputes Act, 1942 was promulgated in April 1942. It was enacted to make provisions for the prevention and settlement of Industrial Disputes and for providing safeguards to the workers.
2. The Trade Unions Act, 1926
The Trade Unions Act, 1926 was enacted to provide for the registration of Trade Unions and to define the law relating to registered Trade Unions.
3. The Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1946
The Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1946 requires employers in Industrial Establishments to define conditions of employment under them. The Act defines the laws which govern the relationship between the employer and the workman in an industrial establishment and includes the elements such as classification of worker, working hours, attendance, suspension, termination, etc.
4. Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020
The Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020 subsumes the following 13 Labour Acts in a single code.
1. The Factories Act, 1948
The Factories Act, 1948 was enacted to consolidate and amend the law regulating labour in factories, with respect to occupational safety and health.
The Factories Act, 1987, amended the Act.
2. The Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970
The Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970 is an Act to regulate the employment of contract labour in specific establishments and also provide for its abolition under certain circumstances. The Act was enacted to prevent the exploitation of contract labourers as there was no existing law.
3. The Mines Act, 1952
The Mines Act, 1952 was enacted to provide measures relating to health, safety, and welfare of workers employed in mines and oil fields. The Act specifies the duties of the employer to manage the mines or mining operations and the health and safety of mines.
4. The Dock Worker (Safety, Health and Welfare) Act, 1986
The Act provides for the health, safety, and welfare of dock workers and matters connected therewith. Any work within the vicinity of any port where loading, unloading, movement, or storage of cargo into or from a ship or other vessel, port, dock, storage place, or landing place comes under the purview of this Act.
5. The Building and Other Construction Workers (Regulation of Employment and Conditions of Service) Act, 1996
This Act was enacted to regulate the employment and condition of service of building and other construction workers and to safeguard their health and provide for their safety and welfare measures and other matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
6. The Plantation Labour Act, 1951
The Plantation Labour Act, 1951 was enacted to regulate the working conditions of workers employed in plantations, and to provide for their welfare. According to the Act, land refers to any piece of land that measures 5 hectares or more that is used to cultivate tea, coffee, cardamom, cinchona, rubber or any other plant, and which employs 15 or more workers on any day of the preceding 12 months.
7. The Inter-state Migrant Workmen (Regulation of Employment and Condition of Service) Act, 1979
This Act was enacted by Parliament to regulate the conditions of service of inter-state labourers. The Act’s objective is to protect migrant workers who are deployed outside their native states in India.
8. The Working Journalists and other News Paper Employees (Conditions of Service and Miscellaneous Provisions) Act, 1955
The objective of this Act is to regulate the services of working journalists and other persons employed in newspaper establishments.
9. The Working Journalists (Fixation of Rates of Wages) Act, 1958
This Act provides for the fixation of rates of wages of working journalists and matters connected therewith.
10. The Cine Workers and Cinema Theatre Workers Act, 1981
The Cine Workers and Cinema Theatre Workers Act, 1981 was enacted to provide for the regulation of the condition of employment of certain cine workers and cinema theatre workers and matters connected therewith.
11. The Motor Transport Workers Act, 1961
The Motor Transport Workers Act, 1961 provides for the welfare of motor transport workers and to regulate the conditions of their work.
12. The Sales Promotion Employees (Condition of Services) Act, 1996
This Act was enacted to regulate certain conditions of service of sales promotion employees in certain establishments. The establishment in this instance applies to every establishment engaged in the pharmaceutical industry.
13. The Beedi and Cigar Workers (Condition of Employment) Act, 1966
The Beedi and Cigar Workers (Condition of Employment) Act, 1966 was enacted to provide for the welfare of the workers employed in establishments that were involved in the manufacture of beedi and cigars, and to regulate the conditions of their work and for matters connected therewith.
These 4 Labour Codes were passed by Parliament but are yet to be implemented. These reforms will lead to a stable atmosphere for businesses to invest in and create a win-win situation for both the employer and the employees.
Other Laws that are mandated
A few more laws that are mandated are briefed below:
1. Apprentices Act, 1961
The Apprentices Act was enacted to regulate and control the training of apprentices in the industry and to utilize the facilities available in the industry for imparting practical training with the view to meeting the requirements of skilled manpower for the industry.
2. The Employees’ Liability Act, 1938
The Employees Liability Act, 1938 was enacted as a protective umbrella for workmen who bring suits for damages for injuries sustained by them against certain defenses of the employer. The Act has been amended in the year 1970 and is applicable throughout India.
3. The Environment Protection Act, 1986
The Environment Protection Act, 1986 was enacted with the main objective to provide protection and improvement of the natural environment and for matters connected therewith. The act empowers the Centre to take all such measures as it deems necessary for the protection of the environment.
4. The Indian fatal Accidents Act, 1855
The Indian Fatal Accidents Act, 1855 was enacted to deal with the recovery of damages for the death of a person caused by a ‘wrongful act, neglect, or default’ of another person.
5. The Personal Injuries (Compensation Insurance) Act, 1963
This Act imposes a liability on the employers to pay compensation to workmen sustaining personal injuries and to provide for insurance for employers against such liability.
6. Public Liability Insurance Act, 1991
This is an Act enacted to provide public liability insurance for the purpose of providing immediate relief to the persons affected by accidents occurring while handling any hazardous substances and for matters connected therewith.
7. The Weekly Holidays Act, 1942
The Weekly Holidays Act, 1942 was enacted to grant weekly holidays to persons employed n shops, restaurants, and theatres without any deduction or abatement of wages. The Act is applicable throughout India but shall come into force only when the state government implements the same through a notification in the gazette.
Conclusion
All these Acts have been enacted with the specific purpose of safeguarding the interests of the workers both in the organized and unorganized sectors. With the Government of India passing the much-awaited Labour Reforms, we can see changes that will empower the worker and at the same time make it easier to do business in India. Human Resources Management teams have to be alert to the ever-changing rules and regulations, and they have to be fully prepared to update these changes as and when they occur.
GetifyHR has been supporting its clients across the country in handling all the relevant laws. With our hugely successful Payroll Outsourcing module, we have been able to handle these laws across industries and have assisted our clients to be fully compliant, always. Our cloud-based outsourcing module is a fully integrated package that can handle all aspects of Payroll including the generation of Payslips, Managing Leave and Attendance, Statutory Compliance requirements, and Recruitment. We are fully prepared to support existing clients and prospective clients in handling the new Labour Codes once the Government implements them. Contact us for more information.